How To Tell If A Lead Acid Battery Is Fully Charged?
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-20 Origin: Site
Introduction
Lead-acid batteries power everything from vehicles to backup systems, making them essential in daily life. But how can you tell if one is fully charged? In this article, we’ll explore the key indicators and methods for checking the charge level of a lead-acid battery. You’ll learn practical tips for maintaining its health and ensuring longevity.
Understanding Lead Acid Battery Charging Process
The Three-Stage Charging Process
Lead-acid batteries follow a specific charging process, typically involving three stages:
1. Constant Current: The charging starts with a steady current, which gradually raises the voltage of the battery. During this phase, about 70% of the battery’s charge is completed. It typically takes 5 to 8 hours.
2. Topping Charge: After reaching the initial voltage limit, the current decreases, allowing the battery to charge more slowly. This stage ensures the battery reaches full capacity without overcharging. It takes another 7 to 10 hours.
3. Float Charge: The final stage keeps the battery at its fully charged state by providing a small, constant charge to offset the natural self-discharge. This helps maintain a full charge without overcharging.
Key Voltage Ranges in the Charging Process
Voltage is a key indicator during the charging process:
● During the constant current stage, the voltage rises steadily.
● When the battery approaches full charge, the voltage should reach between 2.30V and 2.45V per cell (for a 12V system, that’s about 13.8V to 14.7V).
● When the battery is fully charged, the voltage will stabilize at around 2.25V per cell (about 13.5V for 12V systems).
How Charging Voltage Affects Battery Health
The charging voltage plays a significant role in battery health. Overcharging (voltage too high) can cause gassing, excessive heat, and electrolyte loss, damaging the battery. On the other hand, undercharging (voltage too low) prevents the battery from reaching its full capacity and can cause sulfation, reducing the battery’s life.
Key Indicators of a Fully Charged Lead Acid Battery
Voltage-Based Indicators
The simplest way to determine if a lead acid battery is fully charged is by measuring its voltage. Here are key voltage ranges to know:
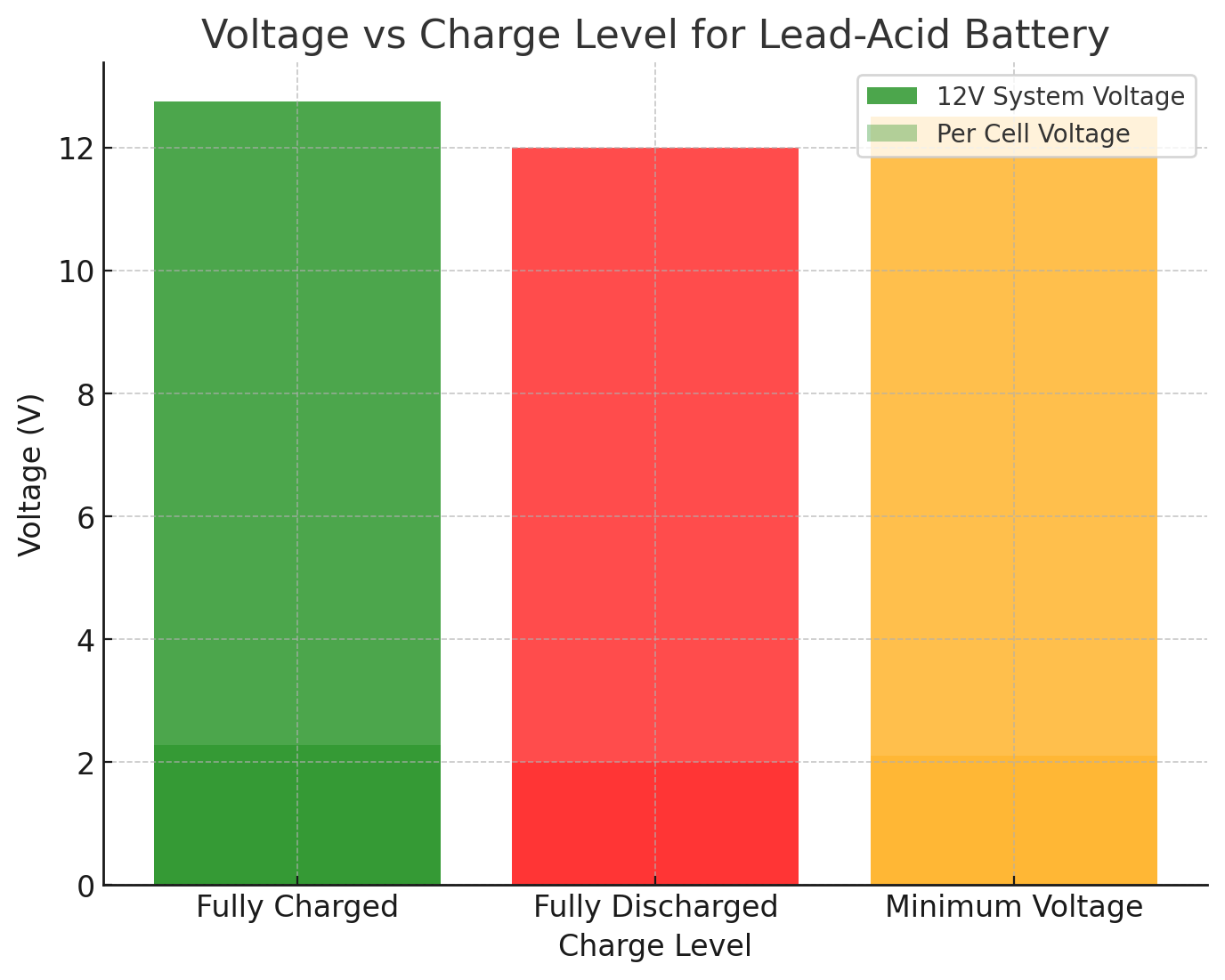
● 12.7V to 12.8V: Fully charged.
● 12.0V: The battery is considered fully discharged.
● 12.5V: This is the minimum voltage to maintain battery health.
If the voltage is near the upper end of the range, the battery is fully charged.
Battery Charge Level | Voltage (12V System) | Voltage (Per Cell) |
Fully Charged | 12.7V - 12.8V | 2.25V - 2.30V |
Fully Discharged | 12.0V | 2.00V |
Minimum Voltage | 12.5V | 2.10V |
Current Drop as a Charging Indicator
As the battery nears full charge, the current supplied to it decreases. During the constant current stage, the charging current is high, but as the topping charge stage begins, the current begins to drop. When the current decreases to about 3-5% of the battery’s capacity, the battery is fully charged.
The Role of the State of Charge (SoC) Indicator
Many modern lead acid batteries feature an integrated State of Charge (SoC) indicator. This can be a simple LED light or a gauge showing the charge level. Green typically means fully charged, yellow or red indicates charging is still needed, and sometimes flashing lights suggest the battery requires maintenance.
Accurate Methods for Determining Full Charge
Using a Multimeter for Voltage Measurements
To measure the voltage, use a multimeter:
1. Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage.
2. Place the red probe on the positive terminal and the black probe on the negative terminal.
3. Read the voltage. If it’s between 12.7V and 12.8V, your battery is fully charged.
Note: It’s important to allow the battery to rest for a few hours before taking measurements, as this ensures an accurate reading.
Hydrometer for Specific Gravity Measurement
A hydrometer can measure the specific gravity of the battery’s electrolyte. As the battery charges, the sulfuric acid concentration increases, which makes the electrolyte denser. A fully charged battery will have a specific gravity reading of 1.265 or higher (at 26°C or 78°F). If the reading is lower, the battery is not fully charged.
Open Circuit Voltage Method
The open circuit voltage (OCV) method measures the voltage of a resting battery with no load applied. After charging, let the battery rest for at least 4 hours to ensure an accurate OCV. At this point, a voltage reading of 12.7V to 12.8V indicates a full charge.
Advanced Methods: Impedance Spectroscopy
Impedance spectroscopy is a more sophisticated technique used in battery management systems. It measures the battery’s impedance (resistance to current flow) and provides a detailed picture of its state of charge and health. While not commonly used for everyday applications, it’s useful for large-scale systems and research purposes.
Common Charging Issues and How to Avoid Them
Overcharging and Gassing Risks
Overcharging a lead acid battery can cause the electrolyte to bubble, releasing hydrogen and oxygen gases. This can lead to water loss, damage to the battery plates, and reduced capacity. Always use chargers with built-in voltage regulation to prevent overcharging.
How Temperature Affects Charging Accuracy
Temperature plays a key role in charging accuracy. At higher temperatures, the battery’s voltage will rise, and at lower temperatures, it will drop. For every degree above 25°C (77°F), the charge voltage should be reduced by 3mV per cell, and for every degree below 25°C, the charge voltage should be increased by 3mV per cell.
Temperature (°C) | Voltage Adjustment (mV per cell) | Recommended Charge Voltage (Per Cell) |
0°C | +3mV | 2.40V |
25°C | No adjustment | 2.30V |
40°C | -3mV | 2.20V |
The Importance of Float Charging in Maintenance
Float charging is critical in maintaining a fully charged lead acid battery without overcharging. It compensates for the battery’s self-discharge, keeping it at full charge indefinitely. If the charger lacks float charge capabilities, consider removing the battery from the charger once it’s fully charged to avoid overcharging.
Preventative Maintenance for Lead Acid Batteries
Regular Voltage Checks
To ensure your battery stays in good condition, regularly check its voltage. Doing so every 3-6 months can help detect any early signs of issues, such as poor charging or internal resistance.
Watering and Electrolyte Levels
For flooded lead acid batteries, it’s crucial to maintain proper electrolyte levels. Over time, water evaporates from the electrolyte, especially if the battery has been overcharged. Always use distilled or deionized water to refill the electrolyte after charging.
Storing Batteries Properly
When storing a lead acid battery for extended periods, make sure it is fully charged to prevent sulfation. If you’re storing the battery in a cold environment, consider using a battery maintenance charger to keep the battery at optimal charge levels.
What to Do if Your Battery Isn’t Fully Charged
Troubleshooting Charging Problems
If your battery is not charging fully, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
● Check the charger’s voltage settings: Ensure the charger is providing the correct voltage range for your battery.
● Examine for damage: Inspect the battery and terminals for any visible signs of damage or corrosion.
● Consider replacing the charger: If the charger is old or malfunctioning, it may be unable to charge the battery correctly.
When to Replace Your Lead Acid Battery
A lead acid battery typically lasts 3-5 years, depending on usage and maintenance. If you consistently face issues like slow charging, reduced voltage, or gassing, it may be time to replace the battery. Aging batteries may no longer hold a full charge, leading to frequent recharging and shorter battery life.
Conclusion
Knowing how to determine if a lead acid battery is fully charged is crucial for its health and longevity. Methods like voltage measurements, current drop indicators, and impedance spectroscopy are effective for monitoring your battery’s state of charge. Regular maintenance, proper charging practices, and troubleshooting ensure your battery stays in optimal condition.JUJIANG POWER offers high-quality lead-acid batteries designed for durability and performance. Their products provide excellent value through advanced design, ensuring longer battery life and reliable service.
FAQ
Q: How can I tell if my lead-acid battery is fully charged?
A: You can check the voltage of your lead-acid battery using a multimeter. A fully charged battery should read between 12.7V and 12.8V.
Q: What is the best way to check if a lead-acid battery is charged?
A: The most reliable method is to measure the open circuit voltage (OCV) after the battery has rested for a few hours.
Q: Why does my lead-acid battery not reach full charge?
A: Issues like improper charging settings, a faulty charger, or a damaged battery can prevent your lead-acid battery from fully charging.
Q: How long does it take to fully charge a lead-acid battery?
A: A typical lead-acid battery takes 12-16 hours to fully charge using the constant current method, though it depends on the charger and battery size.
Q: What are the signs of an overcharged lead-acid battery?
A: Overcharging causes gassing, electrolyte loss, and excess heat. If you notice these, it could mean your lead-acid battery is overcharged.
Q: How often should I check the charge level of my lead-acid battery?
A: It’s good practice to check the charge level every 3-6 months to ensure your lead-acid battery stays healthy and maintains its charge.
Q: Can temperature affect my lead-acid battery's charge?
A: Yes, temperature fluctuations can affect charging accuracy. Warmer temperatures require lower voltage, while colder temperatures need higher voltage.
Q: What happens if a lead-acid battery is undercharged for too long?
A: Prolonged undercharging can lead to sulfation, which decreases the battery’s capacity and lifespan.



